Is Your Business at Risk?
Discover the Shocking Truth About Staffing Piggybacking.
Is Your Business at Risk?
Discover the Shocking Truth About Staffing Piggybacking.
Staffing Agency Fraudsters Are Insanely Making Money Off You and the Backs of Workers They Provide! This Must Stop!
Piggybacking is a serious threat to businesses, putting them at risk of legal trouble, financial loss, and damage to their reputation. Despite its illegality, piggybacking is widespread and regulatory agencies aren't doing enough to stop it.
Businesses that get involved in piggybacking face lawsuits, hefty fines, and financial ruin. They may think they're saving money, but they're actually setting themselves up for disaster. Real-life examples show how easily businesses can fall victim to deceitful staffing agencies promising cheap deals.
Without strong regulations, piggybacking is becoming more common, leaving businesses vulnerable to exploitation. It's crucial for businesses to understand the risks and take action to protect themselves before it's too late.
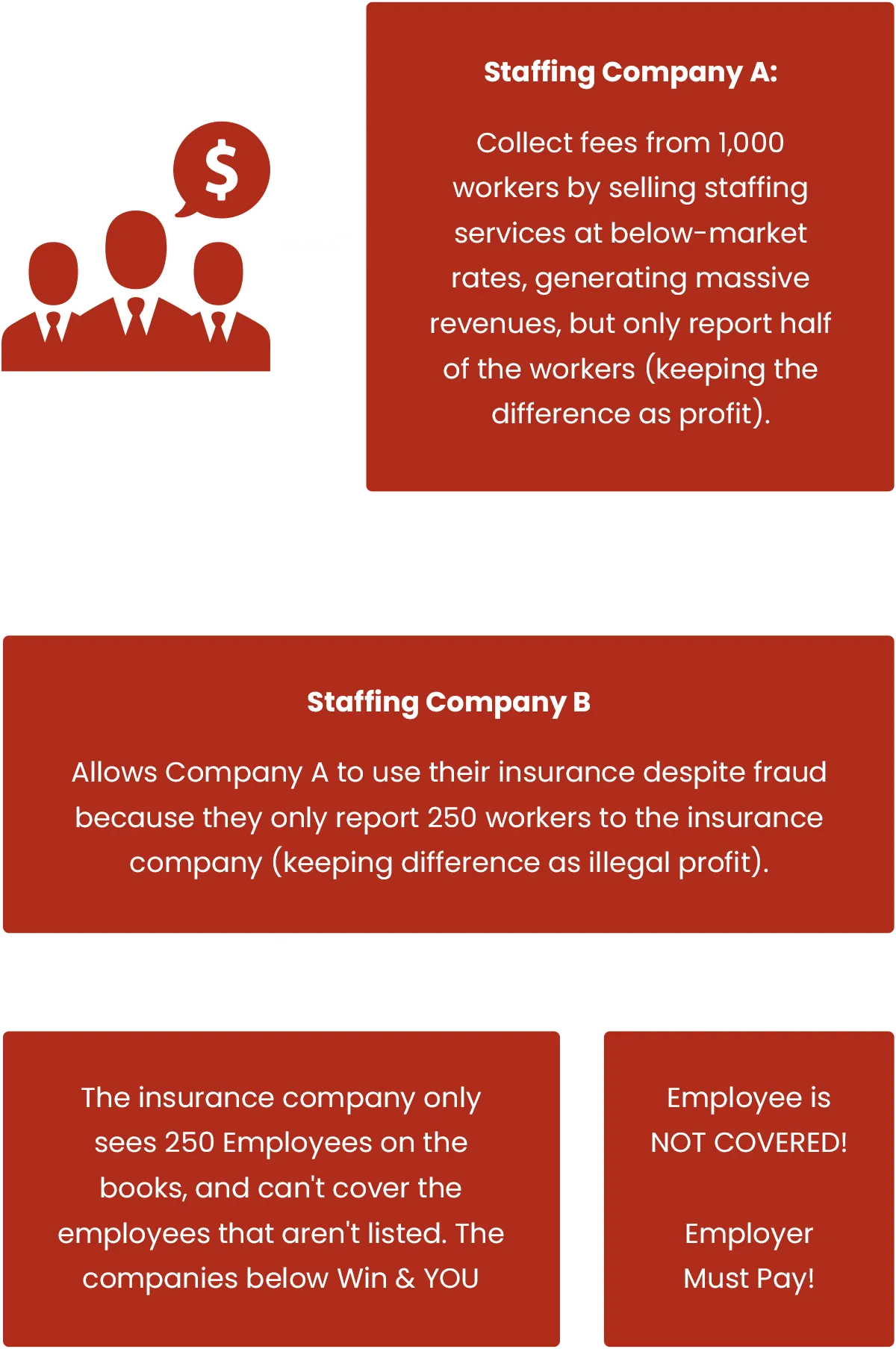

Fraudulent agencies often use deceptive tactics to trick employers and avoid detection.
1
Falsifying Certificates
They may provide fake insurance certificates that appear legitimate but don't actually provide coverage.
2
Underreporting Payroll
Fraudulent agencies may manipulate payroll records to reduce reported payroll, leading to lower insurance premiums.
3
Misrepresentation
They may mislead employers about their coverage status or the extent of their insurance, creating a false sense of security.
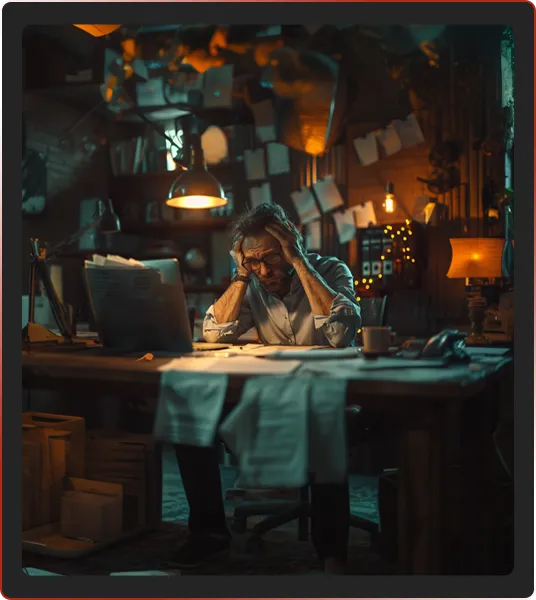

Businesses must take proactive steps to protect themselves from these deceptive practices.

1
Verify Certificates
Always verify the authenticity of insurance certificates by contacting the insurance provider directly.
2
Conduct Due Diligence
Thoroughly vet staffing agencies before partnering with them, checking their reputation, credentials, and compliance history.
3
Stay Informed
Stay up-to-date on industry regulations and trends to spot red flags and avoid falling victim to fraudulent schemes.
Staffing Agency Fraudsters Are Insanely Making Money Off You and the Backs of Workers They Provide! This Must Stop!

Piggybacking is a serious threat to businesses, putting them at risk of legal trouble, financial loss, and damage to their reputation. Despite its illegality, piggybacking is widespread and regulatory agencies aren't doing enough to stop it.
Businesses that get involved in piggybacking face lawsuits, hefty fines, and financial ruin. They may think they're saving money, but they're actually setting themselves up for disaster. Real-life examples show how easily businesses can fall victim to deceitful staffing agencies promising cheap deals.
Without strong regulations, piggybacking is becoming more common, leaving businesses vulnerable to exploitation. It's crucial for businesses to understand the risks and take action to protect themselves before it's too late.

Fraudulent agencies often use deceptive tactics to trick employers and avoid detection.

1
Falsifying Certificates
They may provide fake insurance certificates that appear legitimate but don't actually provide coverage.
2
Underreporting Payroll
Fraudulent agencies may manipulate payroll records to reduce reported payroll, leading to lower insurance premiums.
3
Misrepresentation
They may mislead employers about their coverage status or the extent of their insurance, creating a false sense of security.
Businesses must take proactive steps to protect themselves from these deceptive practices.

1
Verify Certificates
Always verify the authenticity of insurance certificates by contacting the insurance provider directly.
2
Conduct Due Diligence
Thoroughly vet staffing agencies before partnering with them, checking their reputation, credentials, and compliance history.
3
Stay Informed
Stay up-to-date on industry regulations and trends to spot red flags and avoid falling victim to fraudulent schemes.
Act now to protect your business from the dangers of staffing piggybacking. Don't wait until it's too late. Verify your staffing agency's insurance coverage today at CheckMyCert.org. Click below to take action and safeguard your business.
Act now to protect your business from the dangers of staffing piggybacking. Don't wait until it's too late. Verify your staffing agency's insurance coverage today at CheckMyCert.org. Click below to take action and safeguard your business.
FAQs
1 What is piggybacking in the context of workers' compensation insurance?
Piggybacking refers to the practice of a staffing agency or employer using another company's workers' compensation insurance policy to cover its employees, rather than obtaining its own coverage. This can be done without the knowledge or consent of the insurance provider and often involves fraudulent activity.
2 How does piggybacking impact businesses and employees?
Piggybacking poses significant risks to both businesses and employees. In the event of an injury or workers' compensation claim, businesses relying on piggybacked insurance may find themselves without adequate coverage, exposing them to financial liabilities and legal consequences. Employees may also face challenges in receiving compensation for workplace injuries if the insurance coverage is invalid or insufficient.
3 What are some common tactics used by fraudulent agencies to engage in piggybacking?
Fraudulent agencies may use various tactics to deceive employers and evade detection. These can include falsifying insurance certificates, misrepresenting their coverage status, or engaging in identity theft to access legitimate policy information.
4 How can businesses protect themselves against piggybacking?
Businesses can take proactive steps to protect themselves against piggybacking by verifying the authenticity of insurance certificates provided by staffing agencies or contractors. This can involve contacting the insurance provider directly to confirm coverage and ensuring that the policy aligns with the scope of work and number of employees involved.
5 How prevalent is piggybacking in the business world?
Engaging in piggybacking can have serious legal and financial repercussions for businesses involved. In addition to potential fines and penalties for non-compliance with insurance regulations, businesses may be held liable for any workplace injuries or claims that arise without adequate coverage. This can result in costly legal battles, reputational damage, and even bankruptcy in severe cases.
6 How does piggybacking impact businesses and employees?
While exact statistics on piggybacking are difficult to determine due to its clandestine nature, it is believed to be a widespread problem affecting businesses in various industries. Reports of fraudulent activities and regulatory violations related to piggybacking continue to emerge, highlighting the need for heightened awareness and vigilance among employers.
7 Where can businesses go for assistance or further information on piggybacking?
Businesses seeking assistance or further information on piggybacking can reach out to regulatory agencies, industry associations, or legal professionals specializing in workers' compensation insurance. Additionally, online resources, educational materials, and training programs may offer valuable insights and guidance on how to detect and prevent piggybacking schemes.

FAQs
1 What is piggybacking in the context of workers' compensation insurance?
Piggybacking refers to the practice of a staffing agency or employer using another company's workers' compensation insurance policy to cover its employees, rather than obtaining its own coverage. This can be done without the knowledge or consent of the insurance provider and often involves fraudulent activity.
2 How does piggybacking impact businesses and employees?
Piggybacking poses significant risks to both businesses and employees. In the event of an injury or workers' compensation claim, businesses relying on piggybacked insurance may find themselves without adequate coverage, exposing them to financial liabilities and legal consequences. Employees may also face challenges in receiving compensation for workplace injuries if the insurance coverage is invalid or insufficient.
3 What are some common tactics used by fraudulent agencies to engage in piggybacking?
Fraudulent agencies may use various tactics to deceive employers and evade detection. These can include falsifying insurance certificates, misrepresenting their coverage status, or engaging in identity theft to access legitimate policy information.
4 How can businesses protect themselves against piggybacking?
Businesses can take proactive steps to protect themselves against piggybacking by verifying the authenticity of insurance certificates provided by staffing agencies or contractors. This can involve contacting the insurance provider directly to confirm coverage and ensuring that the policy aligns with the scope of work and number of employees involved.
5 How prevalent is piggybacking in the business world?
Engaging in piggybacking can have serious legal and financial repercussions for businesses involved. In addition to potential fines and penalties for non-compliance with insurance regulations, businesses may be held liable for any workplace injuries or claims that arise without adequate coverage. This can result in costly legal battles, reputational damage, and even bankruptcy in severe cases.
6 How does piggybacking impact businesses and employees?
While exact statistics on piggybacking are difficult to determine due to its clandestine nature, it is believed to be a widespread problem affecting businesses in various industries. Reports of fraudulent activities and regulatory violations related to piggybacking continue to emerge, highlighting the need for heightened awareness and vigilance among employers.
7 Where can businesses go for assistance or further information on piggybacking?
Businesses seeking assistance or further information on piggybacking can reach out to regulatory agencies, industry associations, or legal professionals specializing in workers' compensation insurance. Additionally, online resources, educational materials, and training programs may offer valuable insights and guidance on how to detect and prevent piggybacking schemes.

